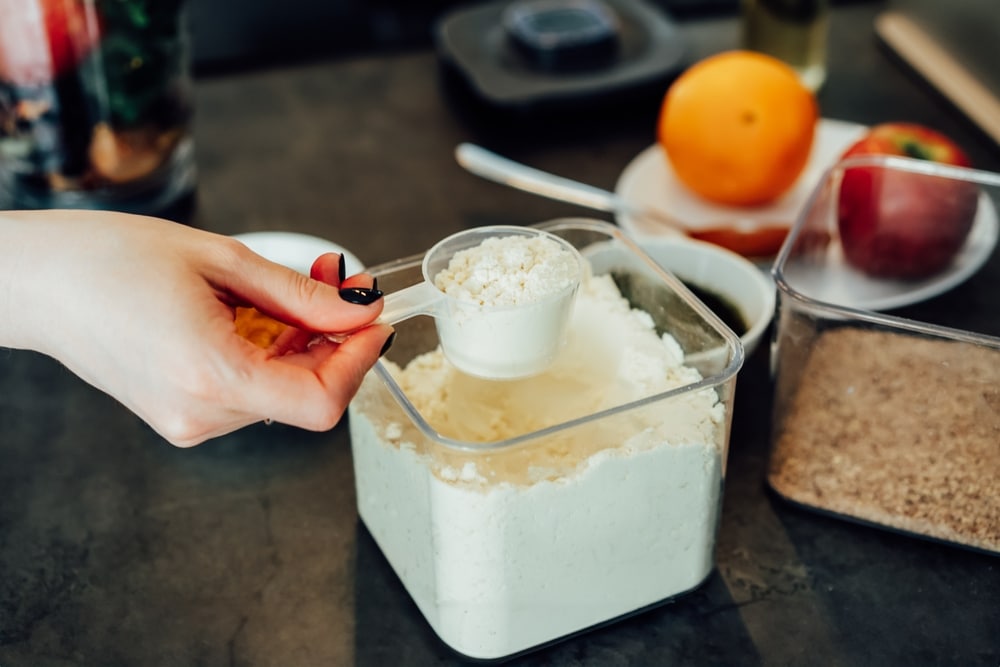
Pea protein powder is quickly becoming a popular choice for fitness enthusiasts and health-conscious individuals. It is free from gluten and dairy, and its benefits extend to heart health, kidney function, and weight management.
While it’s possible to meet your protein needs through a balanced diet, real life often complicates meal prep. This is where protein powder, especially in smoothies, can come in handy, providing a quick protein boost with minimal effort.
Research shows that consuming protein shortly after a workout can aid in muscle recovery and growth. Preparing a proper meal post-workout can be challenging; a smoothie loaded with pea protein serves as a convenient alternative to replenish nutrients while avoiding a heavy feeling.
Switching up your protein sources is an effective strategy to ensure your body receives the variety it needs for optimal function.
Curious about the benefits of pea protein? Let’s dive deeper into this nutritious option.
What is pea protein?
Protein powders come in several varieties, with whey, soy, and brown rice among the most common. While whey and brown rice protein offer distinct advantages, pea protein has gained traction among those choosing a plant-based diet.
The popularity of pea protein is unsurprising, given its impressive nutritional profile. It stands out as one of the most hypoallergenic protein powders available, containing no gluten, soy, or dairy. This makes it an appealing choice for those with dietary sensitivities.
So, how is it produced? Pea protein is made by grinding yellow split peas into a fine powder, removing starch and fiber to yield a highly concentrated protein isolate. It’s perfect for blending into smoothies, baking, or various recipes to enhance protein content.
Nutrition facts
One major consideration when selecting a protein supplement is whether it is a complete protein source. A complete protein contains all nine essential amino acids that the body cannot synthesize and must obtain through dietary sources.
Contrary to some beliefs, pea protein is not the only plant-based source boasting a complete amino acid profile. Both hemp and brown rice proteins also offer a full spectrum of amino acids, though brown rice is slightly low in lysine compared to whey protein.
Pea protein has a nearly complete profile, missing only a few nonessential and conditional amino acids. This highlights the importance of variety in your protein sources for comprehensive benefits.
Regularly incorporating pea protein into your diet can enhance muscle building, fat burning, and cardiovascular health.
Examining the nutrition facts reveals its impressive profile. Just one serving of pea protein powder delivers:
- 99.9 calories
- 2 grams carbohydrates
- 0 grams sugar
- 1 gram fiber
- 1.5 grams fat
- 21 grams protein
- 6.3 milligrams iron (35% DV*)
- 260 milligrams sodium (11% DV)
- 20 milligrams calcium (2% DV)
*Based on a daily intake of 2,000 calories.
Health benefits
The nutrition profile of pea protein contributes to various health benefits, including weight loss and heart health.
1. Aids weight management
Pea protein can be a valuable asset for those looking to shed pounds. Studies indicate that a high-protein breakfast with pea protein can enhance energy expenditure and fat oxidation.
Neglecting protein intake can hinder weight loss efforts. Aiming for 0.8 to 1.6 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight daily can aid muscle growth and fat loss. For a 140-pound individual (approximately 64 kilograms), this translates to about 51 to 103 grams of protein daily.
Pea protein also helps reduce ghrelin levels, the hormone that drives hunger, which can help control cravings.
2. Supports heart health
Pea protein has been shown to positively impact heart health. An animal study noted that pea protein can lower high blood pressure significantly over an eight-week period.
A human study corroborated these findings, revealing that a three-week regimen of pea protein supplementation resulted in reduced systolic blood pressure.
Additionally, a study published in the American Journal of Epidemiology found that a long-term intake of plant-based proteins correlates with lower coronary heart disease risk.
3. May promote kidney function
Research suggests that pea protein may help delay or prevent kidney damage. It can stabilize blood pressure and enhance urine function, facilitating toxin removal from the body.
Another review connected higher plant protein intake to better kidney filtration rates, indicating that consuming more plant proteins can benefit kidney function.
4. Helps increase muscle thickness
There’s a misconception that plant-based proteins like pea protein are inferior for muscle growth compared to dairy proteins. However, studies have demonstrated that pea protein can effectively increase muscle thickness from resistance training.
The high concentration of L-arginine in pea protein may contribute to these muscle-building effects by stimulating human growth hormone production.
5. Helps balance blood sugar levels
Maintaining normal blood sugar levels is essential for overall health. Research indicates that pea protein can assist in regulating blood sugar when consumed with other foods.
6. May enhance physical performance
Similar to whey protein, pea protein can improve physical performance. Research shows that it produces comparable results in strength and workout performance after high-intensity training.
7. Good source of iron
Pea protein is a rich source of iron, crucial for brain health, immune function, and various metabolic processes.
Risks and side effects
While protein powder can conveniently boost intake, it shouldn’t wholly replace protein-rich foods. Whole food sources deliver additional essential nutrients necessary for health.
Pea protein is generally safe, but excessive consumption can lead to potential issues, including weight gain and digestive discomfort for some individuals.
Keep your intake moderate to enjoy the benefits without compromising health.
How to use
Pea protein is widely available in stores and online. Combining it with another protein like brown rice can create a more balanced amino acid profile.
Its mild flavor makes it suitable for smoothies, baked goods, and snacks, allowing for easy incorporation into your diet.
Typically, one serving equals about 27 to 33 grams of pea protein powder. For those with heightened protein needs, refining your intake based on individual activity levels is suggested.
Frequently asked questions
What is pea protein?
Pea protein is a plant-based protein derived from yellow split peas, suitable for those with dietary restrictions such as gluten or dairy intolerances.
Is pea protein a complete protein?
While it contains all nine essential amino acids, it is slightly lower in methionine compared to animal proteins. It is generally adequate when consumed as part of a varied diet.
How much protein is in pea protein powder?
Most varieties deliver 20 to 25 grams of protein per serving, similar to whey protein.
Is pea protein good for you?
Yes, it offers several health benefits while being easy to digest and free from common allergens.
What are the benefits of pea protein?
Pea protein supports muscle growth, satiety, and overall nutrition, making it a potent addition to a balanced diet.
Is pea protein good for muscle building?
Absolutely. It provides essential amino acids that aid in muscle recovery and growth.
How does pea protein compare to whey protein?
Both offer similar protein content, but pea protein is plant-based and may be easier for some to digest.
Is pea protein easy to digest?
Yes, it is generally well-tolerated and less likely to cause bloating.
Can pea protein help with weight loss?
By promoting fullness and supporting muscle preservation, pea protein can aid in weight management efforts.
Does pea protein cause bloating or gas?
Most tolerate it well, but some may experience mild digestive discomfort initially.
Is pea protein safe to use every day?
Yes, it can be safely consumed daily as part of a balanced diet.
Is pea protein suitable for vegans and vegetarians?
Pea protein is entirely plant-based, making it appropriate for vegans and vegetarians.
How should I use pea protein powder?
Mix it into smoothies, shakes, baked goods, or use it in various recipes to enhance protein content.
What is the downside of pea protein?
The primary concern is its lower methionine content relative to animal proteins, but this is easily addressed with a varied diet.
Final thoughts
- Pea protein has gained popularity due to its numerous health benefits.
- Incorporating pea protein into your diet can enhance weight loss efforts, support heart health, and improve kidney function.
- Each serving is a rich source of protein, iron, and essential micronutrients.
- Including a variety of plant-based proteins in your regimen maximizes the unique benefits of each.
- Experiment with pea protein in shakes, desserts, or baked goods for a nutritious addition to your meals.