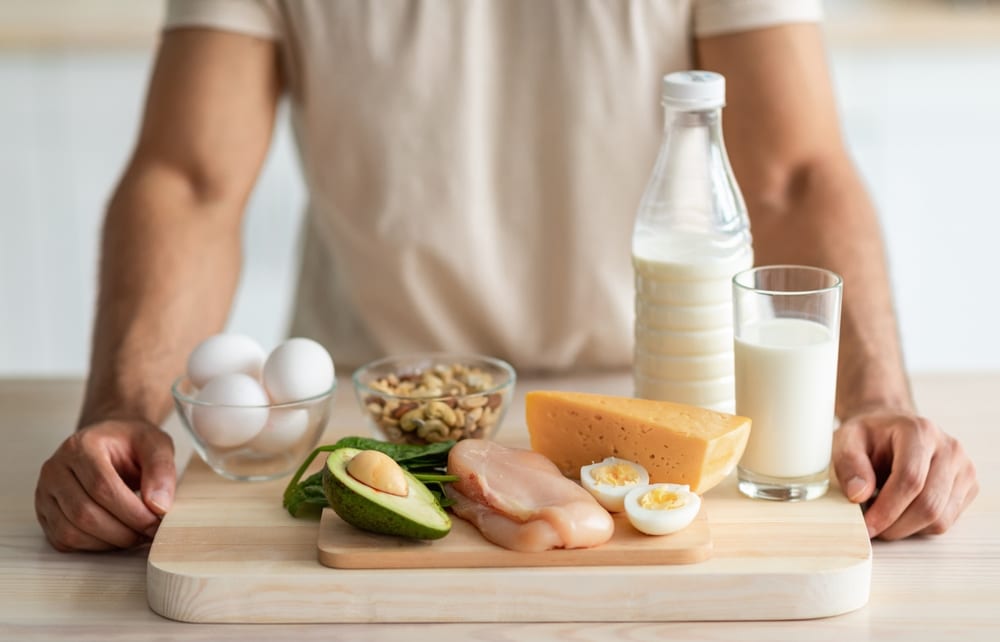
Animal protein is a dominant component of diets worldwide, celebrated for its rich nutrient profile and essential role in health. Its high concentration of vital amino acids, ease of digestion, and significant benefits for muscle health and metabolism make it an appealing choice for many.
In today’s marketplace, animal protein is accessible not just through whole foods but also in various convenient formats, such as protein powders. These supplements have become increasingly popular among fitness enthusiasts, athletes, and anyone eager to elevate their protein intake.
Whether following a high-protein lifestyle, seeking to support healthy aging, or curious about the comparison between animal and plant proteins, this extensive guide highlights the advantages, sources, potential drawbacks, and practical tips for incorporating more animal protein into your meals.
Animal Protein vs. Plant Protein
Animal and plant proteins each can play valuable roles in a balanced diet, yet they differ notably in aspects like digestibility, absorption, and overall nutritional quality.
1. Amino Acid Profile
Animal proteins are recognized as complete proteins because they contain all nine essential amino acids in optimal proportions for human consumption. These amino acids are crucial for muscle repair and hormone production.
While some plant proteins may also be classified as complete, many fall short in specific amino acids, requiring the combination of various plant sources to meet nutritional needs.
2. Digestibility
Animal protein generally ranks higher on digestibility metrics, translating to more efficient absorption and use by the body. Plant proteins often present challenges in digestibility due to compounds like phytates and fiber that may interfere with absorption.
3. Nutrient Density
Beyond protein, animal sources frequently provide other essential vitamins and minerals, including B12, heme iron, zinc, selenium, omega-3 fatty acids, and fat-soluble vitamins. In contrast, plant proteins typically deliver fiber, antioxidants, and phytonutrients.
While both protein types can contribute significantly to a healthy regime, animal protein often offers a more complete amino acid profile and superior digestibility, appealing particularly to athletes and those needing higher protein levels.
Sources
There’s a plethora of high-quality animal protein sources that can enhance your diet, each bringing its unique set of nutrients. Consider these top selections:
1. Poultry
Chicken and turkey are popular, lean options loaded with B vitamins and selenium. When possible, choose free-range varieties for superior quality. A four-ounce cooked chicken breast contains around 29.9 grams of protein, while roasted turkey breast boasts approximately 32.5 grams.
2. Beef
Grass-fed beef serves as a robust protein source, rich in iron, zinc, and conjugated linoleic acid (CLA), which may aid metabolic health. A standard four-ounce serving of grass-fed beef offers approximately 26.1 grams of protein.
3. Eggs
Renowned for their biological value, eggs are a prime protein source and rich in vital nutrients like choline and vitamin D. Two large fried eggs provide roughly 12.5 grams of protein.
4. Dairy
Whole milk, yogurt, and cottage cheese provide excellent sources of branched-chain amino acids, which are essential for muscle recovery. A cup of whole milk contains about 8.1 grams of protein, while three-quarters of a cup of Greek yogurt has approximately 14.9 grams.
5. Fish and Seafood
Fish varieties such as salmon, sardines, and tuna not only deliver protein but are also abundant in omega-3 fatty acids, necessary for cardiovascular and cognitive health. Most seafood types are beneficial sources of animal protein.
6. Animal Protein Powder
Animal protein powders provide a straightforward means to enhance protein intake and support muscle and metabolic health. Multi-animal protein blends are optimal for maximizing the nutritional benefits from diverse sources. Other animal protein choices include:
- Pork
- Lamb
- Bison
- Organ meats, such as liver
- Veal
- Wild game
- Rabbit
- Various cheeses
Benefits
1. Supports Muscle Strength and Maintenance
Animal proteins deliver all essential amino acids and are particularly high in leucine, a key amino acid that triggers muscle protein synthesis. Research supports that incorporating animal protein can help maintain lean muscle mass, optimize recovery, and promote strength, especially in conjunction with resistance training.
2. Promotes Healthy Metabolism
The thermic effect of protein is significantly higher than that of carbohydrates or fats, resulting in more calories being expended during digestion. High-protein diets, particularly those incorporating animal protein, can assist in satiation and metabolic rate, helping maintain blood sugar stability.
3. Encourages Healthy Aging
An adequate protein intake is crucial for preserving muscle mass and bone density as one ages. Studies demonstrate a strong link between higher animal protein consumption and improved metrics of strength and mobility in older populations.
4. Provides Highly Bioavailable Nutrients
Animal protein serves as an enviable source of nutrients that may be sparse in a plant-based diet, including vitamin B12 and omega-3 fatty acids, both vital for cognitive performance, cardiovascular wellness, and energy metabolism.
5. Supports Gut, Skin, and Joint Health
Collagen, a form of animal protein, contains amino acids essential for connective tissue health, joint function, skin elasticity, and gut integrity.
6. Aids in Blood Sugar and Weight Management
Protein stabilizes glucose levels and induces feelings of fullness. High-protein diets have also been shown to help reduce cravings and improve body composition, making it particularly advantageous for individuals managing type 2 diabetes.
7. May Lower Risk of Heart Disease
Unprocessed sources of animal protein like fish and lean meats can bolster cardiovascular health. Diets enriched with nutrient-dense animal protein have been associated with improved cholesterol levels and reduced inflammation.
8. Protects Cognition
Animal proteins are rich in vital nutrients such as DHA and choline, essential for optimal brain health and neurotransmission. Sufficient intake can correlate with enhanced memory and cognitive abilities.
9. May Help Reduce Cancer Risk
High-quality animal proteins like fish and dairy supply nutrients that can boost immune function and cellular repair. Research suggests that these proteins, when integrated into an anti-inflammatory diet, may contribute to a lower risk of cancer.
How to Add Animal Protein to Your Diet
To seamlessly boost your animal protein intake, consider these straightforward strategies:
- Start meals with protein-dense foods like eggs, chicken, or fish.
- Add protein powders to smoothies, oatmeal, or coffee for a swift protein enhancement.
- Snack on high-protein options such as Greek yogurt or hard-boiled eggs.
- Integrate more seafood into your weekly menu.
- Rotate your protein sources weekly for varied nutrition.
Risks and Side Effects
While generally safe, there are considerations to keep in mind with animal protein consumption:
1. Quality Matters
Steer clear of highly processed meats that could contribute to inflammation. Prioritize high-quality animal products, including:
- Grass-fed beef
- Pasture-raised poultry and eggs
- Wild-caught seafood
- Organic dairy
2. Digestive Sensitivities
Some individuals experience discomfort with dairy proteins like whey. In such cases, exploring alternatives like collagen or beef isolate may be beneficial.
3. Overconsumption
Excess protein intake can burden the kidneys in individuals with pre-existing conditions. While most healthy people can manage higher protein intakes, maintaining moderation is essential.
4. Food Allergies
Common allergens include eggs, dairy, and shellfish. Always read labels and introduce new protein sources cautiously if you have known sensitivities.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is animal protein healthier than plant protein?
Both animal and plant proteins have their merits, but animal protein comprises all essential amino acids in ideal ratios, enhancing its bioavailability. Many prefer a combination of both for comprehensive nutrition.
What is the best animal protein powder?
The ideal protein powder is contingent upon individual goals. Popular options include:
- Whey: Excellent for muscle recovery
- Collagen: Beneficial for skin and joint health
- Egg White: Notable for digestibility
- Beef Isolate: A solid choice for those avoiding dairy
How much animal protein should I consume daily?
A guideline is to aim for 0.7 to 1 gram of protein for each pound of your target body weight, adjusted based on age, activity level, and personal health objectives.
Is animal protein bad for heart health?
Whole, minimally processed animal proteins from sources like fish and lean poultry can enhance heart health. However, it’s wise to limit consumption of ultra-processed meats.
Can I use animal protein powder daily?
Definitely. Many incorporate animal-based protein powder into their daily routines, particularly those embracing active lifestyles or with hectic schedules.
Conclusion